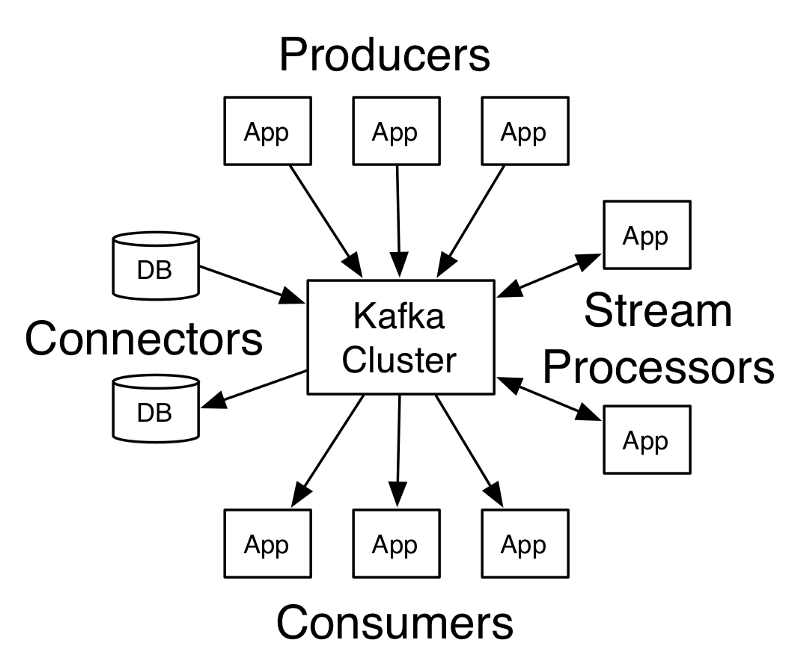
UX Design Trends in 2017
2017 – The Year Of UX
UX Design has totally revolutionized the arena of businesses worldwide. It has enabled business owners to shift the focus away from selling goods or services, and rather focus on selling experiences to the customer. With its growing influence, the field of UX design too is expanding rapidly.
For those who want to know what is in store for 2017 and 2018, here is a quick compilation of the UX design trends that will continue to be popular in 2017 and 2018:
1 – Platform independent UX
As we increasingly move to cross-platform solutions, we are looking to deliver a richer cross-platform experience to users. Be it responsive design to cater to different screen sizes, or fading online-offline channels for generating e-commerce sales, the entire world is now looking to have a contextual yet platform-agnostic user experience to be delivered to customers.
2 – Better personalization
Gone are the days of batch mailing and hoping for great conversions. Today it is all about personalization of the marketing messages after considering the views and opinions of users. For this, marketers will need to reach far and wide and sift through multiple sources of unstructured and structured data like diverse social media feeds.
3 – Move away from general UX
The scope of specialization within the UX domain is fast gaining momentum. As a result, we will see domain-specific UX design expertise emerging for sectors like Artificial Intelligence, Virtual Reality, and within industry verticals like healthcare.
4 – Performance tracking beyond the interface
Traditional metrics like bounce rate, page visit, etc. will hold lesser prominence as performance indicators. Instead, there will be more emphasis on how well an experience was delivered to a customer. Take the case of Snapchat Spectacles. The accessory is great for Snapchat users to interact with the platform without the use of a phone. This merging of an intuitive experience around the way a customer uses a product denotes the overall experience delivered to the Snapchat user.
5 – Merging UX into the employee workflow
A visionary management will seek to integrate UX as a management practice rather than an alienated concept in 2017 and 2018. In this, the management will employ UX and put themselves into the shoes of the employee. This will allow them to know what triggers, incentives, or limitations an employee faces at each stage of a user journey – right from suggesting an idea, to implementing it, and then seeing what happens when they fail. This UX integration will be a great motivation boost for employees to bring out their innovative steak into routine work. This trend of enabling UX design for employees is expected to gain traction in 2017 and 2018.
As evident, the forward- looking trends will play a greater role in helping businesses stay ahead competitively in a crowded digital landscape. Make sure to employ these trends into your next UX design project and enable the much needed competitive edge to your clients.